Pedro Lucas de Resende Melo, Felipe Mendes Boriniy Moacir de Miranda Oliveira Jr.
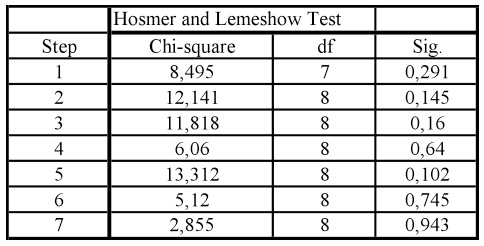
As described above, a model of logistic regression for the tests of the presented hypothesis was executed. The correlations between the independent variable ones show the existence of few statistically significant correlations and when existing they are presented with low intensity which allows to continue the model without incurring into multiple problems. Table 1 shows the significance of a model with the Hosmer and Lemeshow measure of general adjustment, whose focus is not to reject Ho, that is, to prove that significant difference between the observed and previewed classifications does not exist. In this table we observe that the Hosmer and Lemeshow measure does not reject the Ho for the six stages of the model twirled for the method forward stepwise until the last stage that represents the final model.
Table1: Hosmerand LemeshowTest

Sources: Authors
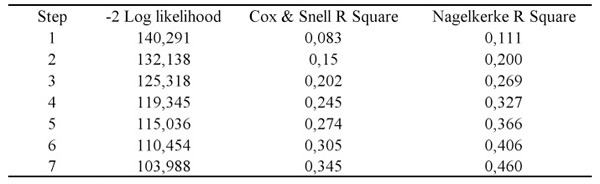
Table 2 shows the measure -2LL, whose value must decrease the measure that new independent variable are placed in the model. In the point where the decrease for new variable ones does not add value to the model, that is the seventh step of the model, we have the measure of end of explanation of the model represented by the measures of the R2, Cox and Snell and R2 of Nagelkerke, considering the last one the best, therefore Cox and Snell do not reach at one. So we can inquire that the obtained model has a power of explanation of the dependent variable one of 46%, a considerable number for applied researches in social sciences.
Table 2: Model Adherence
Sources: Authors
Table 3 presents the obtained model, added to the statistics of significance of each variable one and to the statistics Wald and Ex (B). The statistics WALD also evaluates the significance of the model, which expects high values in the Wald as observed in the table. The Exp (B) shows the impact in the inequality that a variation in one of the variable ones, keeping them very constant. What shows that the chosen strategy and the attended segment are essential variables to explain the composition of the resources, confirming in this way our argument that praises the strategic resources according to the adopted strategy and consequently, the outsource servicing decision or not according to the alignment of the strategic resources with the business focus.
Table 3: Model of Logistic Regression
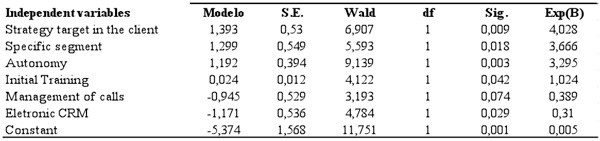
Sources: Authors
In this way the obtained model with a R2 of Nagelkerke of 0,46 supports the H1a hypothesis; H1b; H2 and H3. Outsource servicing call centers are guided for mass segments adopting strategies focused in the product/service supported by strategic resources, coming from the information technology, while own call centers are guided for specific segments adopting strategies focused in the customer and supported by strategic resources coming from the human factor.
Some reflections and comments in relation to the validity of this hypothesis need to be delimited. In relation to the H1a and H1b, the weight in the variability that the variable ones referred to these hypothesis cause, allows inferring a strong alignment in choosing the underlying outsource servicing as a result of the choice of the performance strategy and attended segment.
About what refers to the H2, from the list of the used technologies to deal with customer, two already expected technologies for the fashion of its use in the current enterprise scene are: The CRM and the management of calls. The Voice on IP is another one that does not appear in the model, but separately presents some relation with outsourced service companies focused in the product and mass public.
About what refers to the H3 notices that for own call centers with strategy of focus in the customer and specific public two important daily pay-conditions for the development of the human resources are the autonomy and training.
The autonomy presents in the model with strong power confirming the hypothesis. On the other side, the biggest presence of an initial training that continuous leaves doubts how much the effectiveness of the implementation of strategic of own call centers.
The mooring cable in the strategy of operational efficiency still hinders greater inversion of capital in the formation and development human capital. One is about a task that own call centers needs to surpass if they desire to get significant and compatible returns with outsource servicing call centers.
In this last part of this article we promote some considerations about the findings of these hypotheses and answer the question about when outsourced servicing call center should be adopted.
A first comment coming from the obtained structure of this article and the results relate to the joint of the strategies and the investments in resources. Following the RBV rules the hypothesis show as such theory help to understand the disposal of the investments in resources in core business of the business.
The companies focused in the product adopt the outsourced servicing in their operation; therefore the outsourced ones are capable to provide technological resources, once that, this is the main strategic resource. Therefore, the call center focused in the attendance prefers to keep its services of tele-attendance, because it has greater capacity to promote the strategic development of the human resources than if it was used an outsourced servicing for such operation.
A second point that the hypothesis brings up is the agreement attempt of the call centers strategy in a more detailed way than the vision of the common sense in based on the operational efficiency. The line of reasoning developed in the text and proved in the result does not create objections to the strategy of operational efficiency, but it articulates two strategic exits for a sector where all companies at a first moment focus in their costs. It is about creating "differences in a world of equals". This thought can be extended for other branches of activity that holds in equal way, that is, where at first sight seems that all companies only compete in the same way.
In special the obtained results open wider perspectives for the management of the call center sector in which refers to the competitive strategies. In the same way, it demands the extension of the applicability for other services where informatized operations and directed toward the preceded information by organizational structures that involve the back office and the front office.
Especially in academic literature concerning the activities of call center the paper contributes for the widening of the Batt’s findings, once that she had already found indications of variations of standards of strategic competitiveness in call centers. However, the relation with the resources and mainly the question of the using outsource servicing and the intermediation of the information technology in these services are important contributions on which the Batt’s texts and the referred call centers had not still leaned upon.
Finally, in the management perspective, the hypothesis show to the controlling the outsourced service strategy for their services of tele-attendance are coming well when the strategic focus will be the product, translated by the technology and when the service will be given for a mass segment. On the other hand, it is better to keep an in-house call center if the focus is the attendance to the customer and a specific segment of high value consumption.
Abbad, G. (1999). Um modelo integrado de avaliação de impacto do treinamento no trabalho: IMPACT. Brasília, Tese de Doutorado – Instituto de Psicologia da Universidade de Brasília.
Hax, A. C.; Wilde Ii; D. L. (2001). The delta project: discovering new sources of profitability in a networked economy. New York: Palgrave.
Zuboff, S. (1994). Automatizar/Informatizar: as duas faces da tecnologia inteligente. Revista de Administração de empresas. São Paulo, v34; n.6, 80-91.