

Vol. 39 (Number 28) Year 2018 • Page 37
Irina P. DEVETYAROVA 1; Nina A. YUKHNEV 2A; Oksana S. AGALAKOVA 3; Svetlana P. GORYACHIKH 4; Marina A. SANOVICH 5; Alexandra V. RYATTEL 6
Received: 16/02/2018 • Approved: 25/03/2018
ABSTRACT: The purpose of the work is to substantiate the necessity and to develop recommendations for successful formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new information and communication technologies (ICT). In order to determine the connection between development of the retail sphere and growth of shadow economy in modern Russia, the authors use the methods of regression and correlation analysis for compilation of the model of paired linear regression and calculation of correlation coefficient. The objects of the research are the share of shadow economy in the structure of GDP and the share of retail trade in the structure of GDP. The information and analytical basis of the research consists of statistical and analytical data of the Russian BBC, the Ministry of Finance of the RF, RBC, and the Federal State Statistics Service. The data for 2000-2016 were used during the research. As a result, the authors come to the conclusion that large companies in the retail sphere are difficult to control, so they have wide capabilities in the sphere of shadow economy. It is possible to fight this with highly-effective system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities on the basis of new ICT. The authors offer the concept of formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT and practical recommendation for its application |
RESUMEN: El propósito del trabajo es verificar la necesidad y desarrollar recomendaciones para la formación exitosa del sistema de monitoreo de actividades empresariales en la esfera minorista en la Rusia moderna sobre la base de las nuevas tecnologías de información y comunicación (TIC). Para determinar la conexión entre el desarrollo de la esfera minorista y el crecimiento de la economía sumergida en la Rusia moderna, los autores utilizan los métodos de regresión y análisis de correlación para la compilación del modelo de regresión lineal pareada y el cálculo del coeficiente de correlación. Los objetos de la investigación son la participación de la economía sumergida en la estructura del PIB y la participación del comercio minorista en la estructura del PIB. La información y la base analítica de la investigación consiste en datos estadísticos y analíticos de la BBC rusa, el Ministerio de Finanzas de la RF, RBC y el Servicio de Estadísticas del Estado Federal. Los datos para 2000-2016 se usaron durante la investigación. Como resultado, los autores llegan a la conclusión de que las grandes empresas en la esfera minorista son difíciles de controlar, por lo que tienen amplias capacidades en el ámbito de la economía sumergida. Es posible combatir esto con un sistema altamente efectivo de monitoreo de actividades empresariales sobre la base de nuevas TIC. Los autores ofrecen el concepto de formación del sistema de seguimiento de actividades empresariales en el ámbito minorista en la Rusia moderna sobre la base de nuevas TIC y recomendaciones prácticas para su aplicación |
Entrepreneurship is peculiar for contradictory influence on the modern socio-economic systems, which are largely determined by the context – business climate. In case of favorable business climate, entrepreneurship is commercially attractive, so it develops actively, stimulates growth of population’s employment, increase of tax revenues into the state budget, acceleration of the rate of economic growth, and increase of population’s living standards.
Unfavorable business climate makes the conduct of the official entrepreneurial activities unprofitable, so, in order to keep the target norm business owners use unofficial methods. This leads to emergence and development of shadow (unofficial) economy. This process negatively influences the development of socio-economic systems, as it raises normative risks for entrepreneurs and leads to absence of labor rights for employees.
For the state and society on the whole, shadow economy means reduction of corporate responsibility and the volume of tax revenues into the state budget, due to which the state becomes unable to perform its social responsibilities, which leads to gradual reduction of the population’s living standards. This leads to high topicality and scientific and practical significance of the search for the means of overcoming the shadow economy.
Hypothesis of this research consists in the fact that large industrial companies, being under the control of the state and society, cannot make their business shadow, while medium and small companies in the retail sphere are difficult to control – so they have wide possibilities in the sphere of shadow economy expansion, which could be fought with highly-effective system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities on the basis of new information and communication technologies. The purpose of the work is to substantiate the necessity and to develop recommendations for successful formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT.
For verification of the offered hypothesis and determination of connection between development of the retail sphere and growth of shadow economy in modern Russia, the authors use the methods of regression and correlation analysis, with which they compile the model of paired linear regression and calculate correlation coefficient. The research objects are the share of shadow economy in the structure of GDP (y) and the share of retail trade in the structure of GDP (x).
The information and analytical basis of the research consists of statistical and analytical accounting of the Russian BBC, the Ministry of Finance of the RF, RBC, and Federal State Statistics Service. The data for 2000-2016 were used (Table 1).
Table 1.
Year |
2000 |
2005 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
Share of shadow economy, % of GDP |
40.00 |
42.00 |
47.00 |
48.00 |
48.00 |
51.00 |
54.00 |
58.00 |
62.00 |
Share of retail trade in the structure of GDP, % |
6.34 |
6.78 |
7.39 |
7.52 |
7.74 |
8.01 |
8.45 |
9.11 |
9.70 |
Source: compiled by the authors on the basis of (BBC Russia, 2017),
(Ministry of Finance of the RF, 2017), (Federal State Statistics Service, 2016),
(RBC, Federal State Statistics Service, 2017).
In order to explain the logic of the received results in the process of quantitative (statistical) analysis, the authors use the methods of qualitative analysis – induction, deduction, synthesis analysis of causal connections, and formalization.
The essence, scale, and practical examples of the negative influence of shadow economy on the modern socio-economic systems, as well as the logic of their turning into shadow economy, are studied in the works (Camacho et al., 2017), (Kostakis, 2017), and (Mazhar and Jafri, 2017). Peculiarities of conduct of entrepreneurship in the retail sphere, as well as the place and role of this sphere in formation of GDP, added value, and innovational development of the modern economic systems, are viewed in the works of such scholars as (Pantano and Gandini, 2017a), (Pantano and Gandini, 2017b), (Yilmazkuday, 2017), and (Makarova, 2017).
The theory and methodology of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities are studied in the works (Calabro et al, 2016), (Vera-Baquero et al., 2016), and (Sebu and Ciocarlie, 2015). Actual issues of application and development of modern ICT are studied in (Popkova et al., 2016a), (Ragulina et al., 2015), (Bogoviz et al., 2017), (Orudjev et al., 2016), (Bogdanova et al., 2016), (Popova, et al., 2016b), (Kuznetsov et al., 2016), (Kostikova et al., 2016), and (Simonova et al., 2017).
As a result of the performed overview and analysis of the modern scientific studies and publications on the set topic, we came to the conclusion that the large number of studies is combined with their narrowness. This is a reason for contradictions, irregularities, and gaps in studying the conceptual and applies issues of formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere, which hinders successful solution of the set problem.
As a result of regression analysis, we obtained the following model of paired linear regression: y=6.65+2.49x. The value of the coefficient of independent variable shows that increase of the share of retail trade in Russia by 1% of GDP leads to increase of the share of shadow economy by 2.49% of GDP. Correlation coefficient equals 99.52%. Therefore, connection between the studied indicators is strong and direct, and the regression model is statistically significant.
The determined influence of the retail sphere on shadow economy shows the necessity for formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in this sphere in the interests of preventing its going into shadow. New ICT have large potential here, and we offer the following recommendations for their application.
Firstly, entrepreneurs have to provide highly-effective stimulation of electronic preparation of all economic operations (B2C, B2B, and B2G) of the companies, involved in the retail sphere, as well as increase of corporate social responsibility of these companies. This stimulation may include the following measures:
Secondly, consumers have to provide stimulation of electronic payment for retail products and development of consumer consciousness. This stimulation may include the following measures:
Thirdly, state regulator has to implement modern highly-effective ICT and equipment for authomatization of the process of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere. Modern ICT must provide access to the following operations conducted within monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere:
According to the offered recommendations, we developed the proprietary concept of formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT (Figure 1).
Figure 1
The concept of formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial
activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT
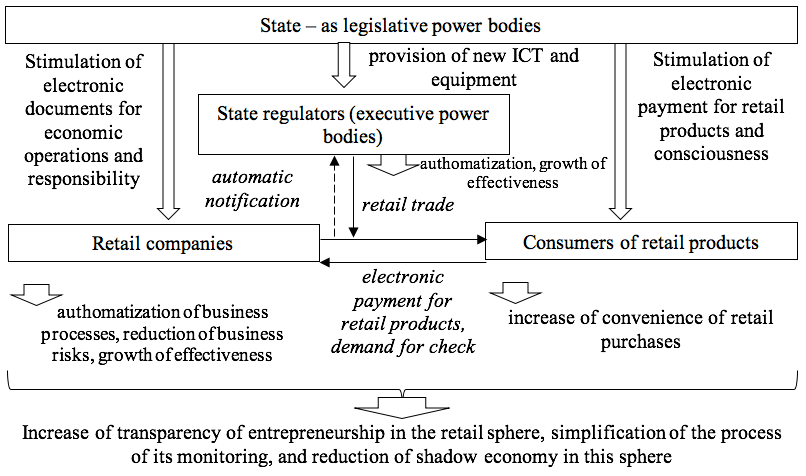
Source: compiled by the authors.
As is seen from Figure 1, according to the offered concept, the state – as legislative power bodies – improves the normative and legal provision in the sphere of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT through practical implementation of the developed recommendations. This will allow for optimization of the process of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere.
As a result of this optimization, consumers will set the demand for electronic payment of retail products, and the companies of the retail sphere will be interested in electronic preparation of all economic operations. This will allow increasing the share of such operations, an additional advantage of which will be automatic electronic (remote) notification of state regulators on their performance.
As a result, state regulators (executive power bodies) will be able to automatize their activities, thus increasing their effectiveness. The companies of the retail sphere will gain profit from authomatization of business processes, reduction of business risks, and growth of effectiveness. Consumers of retail products will get such advantages as increase of convenience of retail purchases. At the scale of socio-economic system, transparency of entrepreneurship in the retail sphere will growth, the process of its monitoring will get simpler, and shadow economy in this sphere will decrease (and in the economic sphere on the whole).
Thus, the authors’ hypothesis is correct – the retail sphere is subject to emergence of shadow economy. The offered concept of formation of the system of monitoring of entrepreneurial activities in the retail sphere in modern Russia on the basis of new ICT allows ensuring comprehensive coverage of this monitoring with reduction of load on state regulators.
An advantage of the offered concept as compared to various state initiatives, which are implemented in modern Russia, is the fact that this concept is based on formation of favorable conditions and profits for all economic subjects from electronic (a priori official) preparation of economic operations. Low effectivenss of mandatory measures (bans, fines, etc.) is obvious, so they should be replaced by measures for stimulation of voluntary electronic preparation of economic operations in the retail sphere, which is stimulates by the developed concept.
BBC: Russia (2017). Research: shadow economy of Russia grows again. URL: http://www.bbc.com/russian/news-41027214 (data accessed: 14.12.2017).
Bogdanova, S.V., Kozel, I.V., Ermolina, L.V., Litvinova, T.N. (2016). Management of small innovational enterprise under the conditions of global competition: Possibilities and threats. European Research Studies Journal, 19(2 Special Issue), p. 268-275.
Bogoviz, A.V., Ragulina, Y.V., Kutukova, E.S. (2017). Ways to improve the economic efficiency of investment policy and their economic justification. International Journal of Applied Business and Economic Research, 15(11), pp. 275-285.
Calabro, A., Lonetti, F., Marchetti, E. (2016). KPI Evaluation of the Business Process Execution through Event Monitoring Activity. Proceedings - 2015 3rd International Conference on Enterprise Systems, ES 2015, 8005a169, с. 169-176.
Camacho, C., Mariani, F., Pensieroso, L. (2017). Illegal immigration and the shadow economy. International Tax and Public Finance, 24(6), с. 1050-1080.
Federal State Statistics Service (2016). Russia in numbers: short statistical collection, Moscow: Federal State Statistics Service.
Kostakis, I. (2017). The impact of shadow economy and/or corruption on private consumption: further evidence from selected Eurozone economies. Eurasian Economic Review, 7(3), p. 411-434.
Kostikova A.V., Tereliansky P.V., Shuvaev A.V., Parakhina V.N., Timoshenko P.N. (2016). Expert Fuzzy Modeling of Dynamic Properties of Complex Systems. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 11 (17), pp. 10601-10608.
Kuznetsov S.Y., Tereliansky P.V., Shuvaev A.V., Natsubize A.S., Vasilyev I.A. (2016). Analysis of Innovate Solutions Based on Combinatorial Approaches. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 11 (17), pp.10222-10230.
Makarova T.V., Palkina M.V., Mironov A.A., Agalakova O.S., Sysolyatin A.V., Kataeva N.N. (2017). The choice of strategic economic areas of a meat processing enterprise. Espasios. Vol. 38. No. 54. P. 33.
Mazhar, U., Jafri, J. (2017). Can the shadow economy undermine the effect of political stability on inflation? empirical evidence. Journal of Applied Economics, .20(2), с. 395-420
Ministry of Finance of the RF (2017). Press center and shadow economy in the country. URL: https://www.minfin.ru/ru/press-center/?id_4=34477&area_id=4&page_id=2119&popup=Y (data accessed: 14.12.2017).
Pantano, E., Gandini, A. (2017a). Exploring the forms of sociality mediated by innovative technologies in retail settings. Computers in Human Behavior, 77, p. 367-373.
Pantano, E., Gandini, A. (2017b). Innovation in consumer-computer-interaction in smart retail settings. Computers in Human Behavior, 77, p. 365-366.
Popkovа, Е.G., Chechina, О.S., Abramov, S.А. (2016a). Problem of the Human Capital Quality Reducing in Conditions of Educational Unification / Е. G. Popkova, // Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6 (3), pp. 95-100.
Popova, L.V., Popkova, E.G., Dubova, Y.I., Natsubidze, A.S., Litvinova, T.N. (2016b). Financial mechanisms of nanotechnology development in developing countries. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences, 11(4), pp. 584-590.
Ragulina, Y.V.; Stroiteleva, E.V.; Miller, A.I. (2015). Modeling of integration processes in the business structures. Modern Applied Science, 9 (3),pp. 145-158.
RBC, Federal State Statistics Service (2017). Informal economy in Russia grew to a new record. URL: https://www.rbc.ru/economics/17/04/2017/58f4b8789a7947c1418ff1af (data accessed: 14.12.2017).
Sebu, M.L., Ciocarlie, H. (2015). Business activity monitoring solution to detect deviations in business process execution. SACI 2015 - 10th Jubilee IEEE International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Proceedings, 7208243, с. 437-442.
Simonova, E.V., Lyapina, I.R. Kovanova, E.S., Sibirskaya, E.V. (2017). Characteristics of Interaction Between Small Innovational and Large Business for the Purpose of Increase of Their Competitiveness. Russia and the European Union Development and Perspectives, pp. 407-415
Vera-Baquero, A., Colomo-Palacios, R., Molloy, O. (2016). Real-time business activity monitoring and analysis of process performance on big-data domains. Telematics and Informatics, 33(3), p. 793-807.
Yilmazkuday, H. (2017). Anti-Crime Laws and Retail Prices. Review of Law and Economics, 13(3), 20160003.
1. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia. Contact e-mail: 1982nastya1982@mail.ru
2. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia.
3. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia.
4. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia.
5. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia.
6. Vyatka State University, Kirov, Russia.